Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
Acetaminophen DC 90
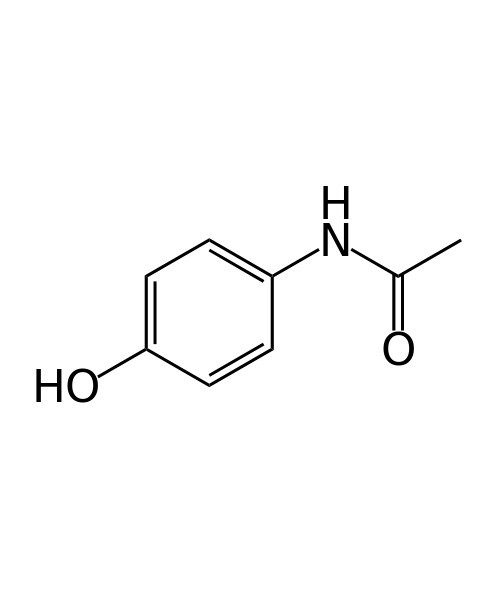
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen or APAP, is a medication used to treat pain and fever.[9] It is typically used for mild to moderate pain.[9] Evidence of benefit in fever for children is poor.[10] It is often sold in combination with other ingredients such as in many cold medications.[9] In combination with opioid pain medication, paracetamol is used for more severe pain such as cancer pain and after surgery.[11] It is typically used either by mouth or rectally but is also available intravenously.[9][12] Effects last between two and four hours.[12]
47

Make an enquiry for this product
Category: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Starting at
Product Description
| N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethanamide N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide |
| Pronunciation | Paracetamol /ˌpærəˈsiːtəmɒl/ or /ˌpærəˈsɛtəmɒl/ Acetaminophen i/əˌsiːtəˈmɪnəfᵻn/ |
| Trade names | Tylenol, Panadol, others[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a681004 |
| Licence data | US FDA:link |
| Pregnancy category |
AU: A US: C (Risk not ruled out) Not tested but seems to be safe |
| Legal status | AU: Unscheduled UK: General sales list (GSL, OTC) US: OTC |
| Routes of administration |
Oral, rectal, intravenous |
| Bioavailability | 63–89%[2]:73 |
| Protein binding | 10–25%[3] |
| Metabolism | Predominantly in the liver[4] |
| Metabolites | APAP gluc, APAP sulfate, NAPQI, APAP-GSH, APAP-cys[5] |
| Biological half-life | 1–4 hours[4] |
| Excretion | Urine (85–90%)[4] |
| CAS Number | 103-90-2 |
| ATC code | N02BE01 |
| PubChem | CID: 1983 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 5239 |
| DrugBank | DB00316 |
| ChemSpider | 1906 |
| UNII | 362O9ITL9D |
| KEGG | D00217 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:46195 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL112 |
| PDB ligand ID | TYL (PDBe, RCSB PDB) |
| Formula | C8H9NO2 |
| Molecular mass | 151.163 g/mol |
| SMILES[show] | |
| InChI[show] | |
| Density | 1.263 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 169 °C (336 °F) [7][8] |
| Boiling point | 420 °C (788 °F) |
| Solubility in water | 12.78[6] mg/mL (20 °C) |
46