Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
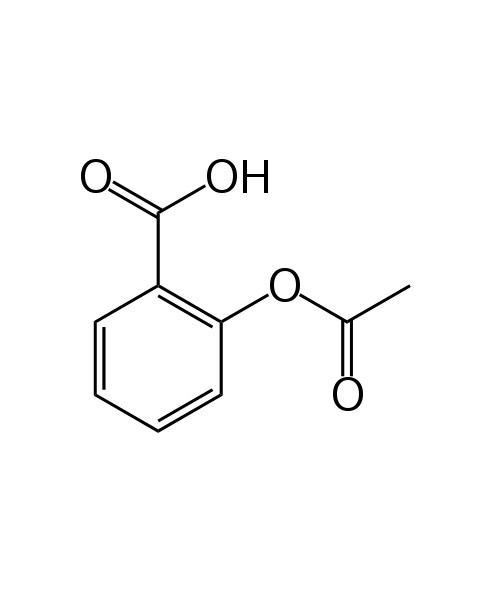
Acetylsalicylic Acid
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a medication, often used to treat pain, fever, and inflammation.[2] Aspirin is also used long-term, at low doses, to help prevent heart attacks, strokes, and blood clot formation in people at high risk of developing blood clots.[3] Low doses of aspirin may be given immediately after a heart attack to reduce the risk of another heart attack or the death of heart tissue.[4][5] Aspirin may be effective at preventing certain types of cancer, particularly colorectal cancer.[6][7][8]

Make an enquiry for this product
Category: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Starting at
Product Description
| 2-(acetoxy)benzoic acid |
| Pronunciation | acetylsalicylic acid /əˌsiːtəlˌsælᵻˈsɪlᵻk/ |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682878 |
| Pregnancy category |
AU: C US: C (Risk not ruled out) D in the 3rd trimester |
| Legal status |
AU: S2 (Pharmacy only) except when given intravenously (in which case it is schedule 4), used in animal medicine (schedule 5/6) or when the dose is higher than usual. UK: General sales list (GSL, OTC) US: OTC |
| Routes of administration |
Most commonly oral, also rectal, lysine acetylsalicylate may be given intravenously or intramuscularly |
| Bioavailability | 80–100%[1] |
| Protein binding | 80–90%[2] |
| Metabolism | Hepatic, (CYP2C19 and possibly CYP3A), some is also hydrolysed to salicylate in the gut wall.[2] |
| Biological half-life | Dose-dependent; 2–3 hours for low doses, 15–30 hours for large doses.[2] |
| Excretion | Urine (80–100%), sweat, saliva, feces[1] |
| CAS Number | 50-78-2 |
| ATC code | A01AD05 B01AC06, N02BA01 |
| PubChem | CID: 2244 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 4139 |
| DrugBank | DB00945 |
| ChemSpider | 2157 |
| UNII | R16CO5Y76E |
| KEGG | D00109 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:15365 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL25 |
| Synonyms | 2-acetoxybenzoic acid acetylsalicylate acetylsalicylic acid O-acetylsalicylic acid |
| PDB ligand ID | AIN (PDBe, RCSB PDB) |
| Formula | C9H8O4 |
| Molecular mass | 180.157 g/mol |
|
SMILES[show] |
|
|
InChI[show] |
|
| Density | 1.40 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 135 °C (275 °F) |
| Boiling point | 140 °C (284 °F) (decomposes) |
| Solubility in water | 3 mg/mL (20 °C) |