Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
Allopurinol
Allopurinol, sold under the brand name Zyloprim and generics, is a medication used primarily to treat excess uric acid in the blood and its complications, including chronic gout.[1] It is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor which is administered orally.
It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, a list of the most important medication needed in a basic health system.[2]

Make an enquiry for this product
Category: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Starting at
Product Description
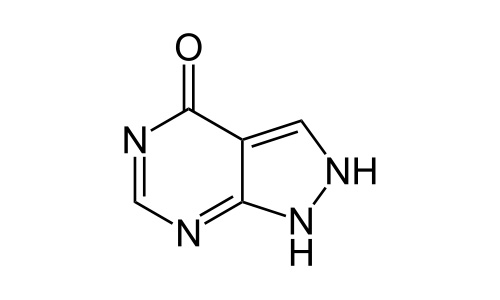
| 1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4(2H)-one |
| Trade names | Zyloprim |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682673 |
| Pregnancy category |
C(USA) |
| Legal status |
UK: POM (Prescription only) US: ℞-only |
| Routes of administration |
tablet (100, 300 mg) |
| Bioavailability | 78±20% |
| Protein binding | Negligible |
| Metabolism | hepatic (80% oxypurinol, 10% allopurinol ribosides) |
| Biological half-life | 2 h (oxypurinol 18-30 h) |
| CAS Number | 315-30-0 |
| ATC code | M04AA01 |
| PubChem | CID: 2094 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 6795 |
| DrugBank | DB00437 |
| ChemSpider | 2010 |
| UNII | 63CZ7GJN5I |
| KEGG | D00224 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:40279 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1467 |
| Formula | C5H4N4O |
| Molecular mass | 136.112 g/mol |
|
SMILES[show] |
|
|
InChI[show] |
|