Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
Fosfomycin Sodium
Fosfomycin (also known as phosphomycin, phosphonomycin and the trade name Monurol and Monuril) is a broad-spectrum antibiotic[1] produced by certain Streptomyces species, although it can now be made by chemical synthesis.

Make an enquiry for this product
Category: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Starting at
Product Description
|
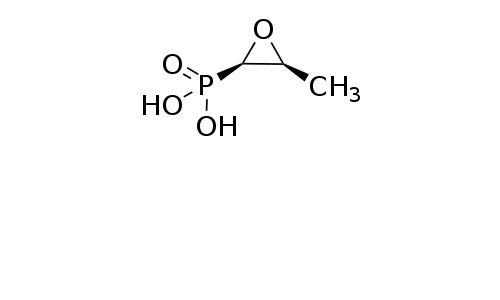
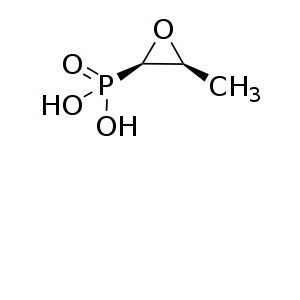
[(2R,3S)-3-methyloxiran-2-yl]phosphonic acid
|
| Trade names | Monurol |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a697008 |
| Pregnancy category |
US: B (No risk in non-human studies) |
| Legal status | US: ℞-only |
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Bioavailability | 30–37% (oral, fosfomycin tromethamine); varies with food intake |
| Protein binding | Nil |
| Metabolism | Nil |
| Biological half-life | 5.7 hours (mean) |
| Excretion | Renal and fecal, unchanged |
| CAS Number | 23155-02-4 78964-85-9 |
| ATC code | J01XX01 |
| PubChem | CID: 446987 |
| DrugBank | DB00828 |
| ChemSpider | 394204 |
| UNII | 2N81MY12TE |
| KEGG | D04253 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:28915 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1757 |
| Formula | C3H7O4P |
| Molecular mass | 138.059 g/mol |
| SMILES[show] | |
| InChI[show] | |
| Melting point | 94 °C (201 °F) |