Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
L-Citrulline
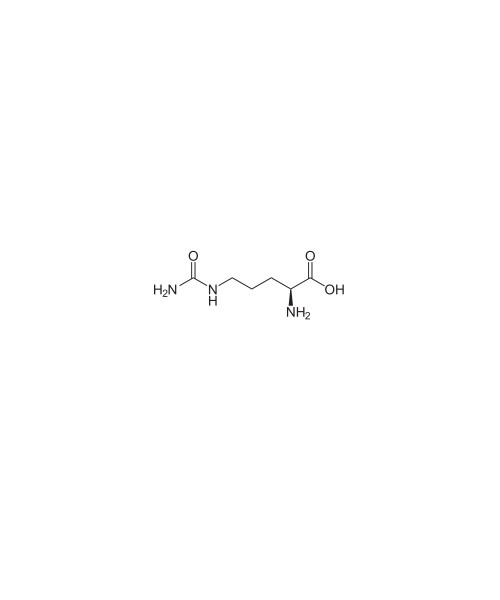
The organic compound citrulline is an α-amino acid. Its name is derived from citrullus, the Latin word for watermelon, from which it was first isolated in 1914 by Koga & Odake. It was finally identified by Wada in 1930.[2] It has the formula H2NC(O)NH(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. It is a key intermediate in the urea cycle, the pathway by which mammals excrete ammonia.
SKU: n/a.
Category: Amino Acids
Starting at $22.75
Product Description
| IUPAC name
2-Amino-5-(carbamoylamino)pentanoic acid[1]
|
|
CAS Number
|
627-77-0 13594-51-9 R 372-75-8 S |
| 3DMet | B01217 |
|
Beilstein Reference
|
1725417, 1725415 R, 1725416 S |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:18211 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL444814 |
| ChemSpider | 810 553200 R 9367 S |
| DrugBank | DB00155 |
| EC Number | 211-012-2 |
|
Gmelin Reference
|
774677 S |
|
IUPHAR/BPS
|
722 |
| Jmol interactive 3D | Image Image |
| KEGG | D07706 |
| MeSH | Citrulline |
| PubChem | 833 637599 R 9750 S |
| UNII | 29VT07BGDA |
|
InChI[show]
|
|
|
SMILES[show]
|
|
|
Chemical formula
|
C6H13N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 175.19 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Odor | Odourless |
| log P | −1.373 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.508 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 11.489 |
|
Specific
heat capacity (C) |
232.80 J K−1 mol−1 |
|
Std molar
entropy (So298) |
254.4 J K−1 mol−1 |
|
Related alkanoic acids
|
N-Acetylaspartic acid |
|
Related compounds
|
Bromisoval |