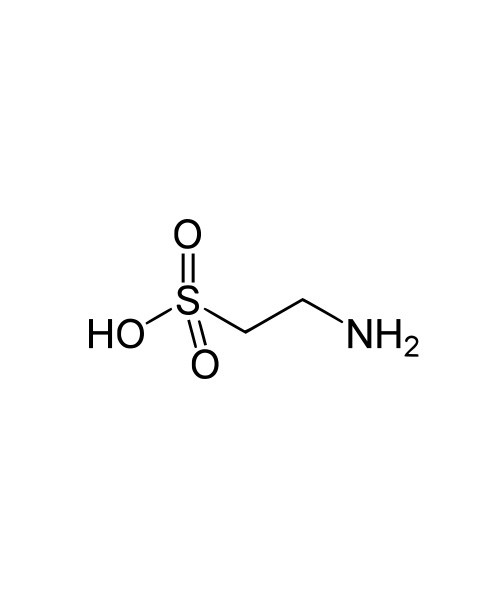
L-Taurine
Taurine (/ˈtɔːriːn/), or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is an organic acid widely distributed in animal tissues. It is a major constituent of bile and can be found in the large intestine, and accounts for up to 0.1% of total human body weight.[1] Taurine has many fundamental biological roles, such as conjugation of bile acids, antioxidation, osmoregulation, membrane stabilization, and modulation of calcium signaling. It is essential for cardiovascular function, and development and function of skeletal muscle, the retina, and the central nervous system. Taurine is unusual among biological molecules in being a sulfonic acid, while the vast majority of biologically occurring acids contain the more weakly acidic carboxyl group. While taurine is sometimes called an amino acid, and indeed is an acid containing an amino group, it is not an amino acid in the usual biochemical meaning of the term, which refers to compounds containing both an amino and a carboxyl group.
Starting at $6.93
Product Description
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-aminoethanesulfonic acid
|
|
| Other names
tauric acid
|
|
CAS Number
|
107-35-7 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:15891 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL239243 |
| ChemSpider | 1091 |
| DrugBank | DB01956 |
|
IUPHAR/BPS
|
2379 |
| Jmol interactive 3D | Image |
| PubChem | 1123 |
| UNII | 1EQV5MLY3D |
|
InChI[show]
|
|
|
SMILES[show]
|
|
|
Chemical formula
|
C2H7NO3S |
| Molar mass | 125.14 g/mol |
| Density | 1.734 g/cm3 (at −173.15 °C) |
| Melting point | 305.11 °C (581.20 °F; 578.26 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | <0, 9.06 |