Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
Lactose Monohydrate M-200
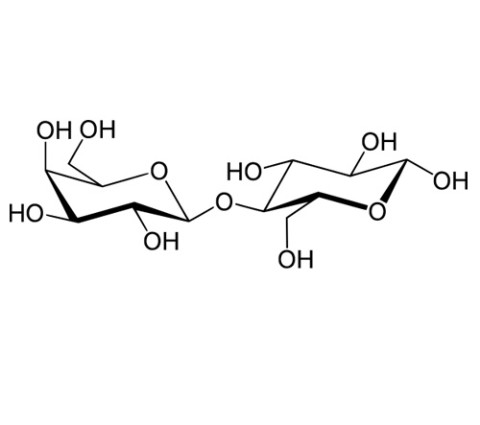
Lactose is a disaccharide sugar derived from galactose and glucose that is found in milk. Lactose makes up around 2–8% of milk (by weight),[3] although the amount varies among species and individuals, and milk with a reduced amount of lactose also exists. It is extracted from sweet or sour whey. The name comes from lac or lactis, the Latin word for milk, plus the -ose ending used to name sugars.[4] It has a formula of C12H22O11 and the hydrate formula C12·11H2O, making it an isomer of sucrose.
SKU: n/a.
Category: Excipients and Additives
Starting at $2.87
Product Description
| IUPAC name
β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-D-glucose
|
|
| Other names
Milk sugar
4-O-β-D-galactopyranosyl-D-glucose |
|
CAS Number
|
63-42-3 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:36218 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL417016 |
| ChemSpider | 5904 |
| EC Number | 200-559-2 |
| Jmol interactive 3D | Image |
| PubChem | 6134←← |
| UNII | 3SY5LH9PMK |
|
InChI[show]
|
|
|
SMILES[show]
|
|
| Chemical formula | C12H22O11 |
| Molar mass | 342.30 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.525 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 202.8 °C (397.0 °F; 475.9 K)[2] |
| Boiling point | 668.9 °C (1,236.0 °F; 942.0 K)[2] |
|
Solubility in water
|
21.6 g/100 mL[1] |
|
Chiral rotation ([α]D)
|
+55.4° |
|
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcHo298) |
5652 kJ/mol, 1351 kcal/mol, 16.5 kJ/g, 3.94 kcal/g |
| NFPA 704 | 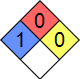 |
| Flash point | 357.8 °C (676.0 °F; 631.0 K)[2] |