Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
Levofloxacin
Levofloxacin (trade names Levaquin (US), Tavanic (EU), and others) is a broad-spectrum antibiotic of the fluoroquinolone drug class,[1] and the levo isomer of its predecessor ofloxacin. Levofloxacin is used alone or in combination with other antibacterial drugs to treat certain bacterial infections including pneumonia,[2] urinary tract infections,[3][4] and abdominal infections.[5] Levofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones are valued for their broad spectrum of activity, excellent tissue penetration, and for their availability in both oral and intravenous formulations.[6]

Make an enquiry for this product
Category: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Starting at
Product Description
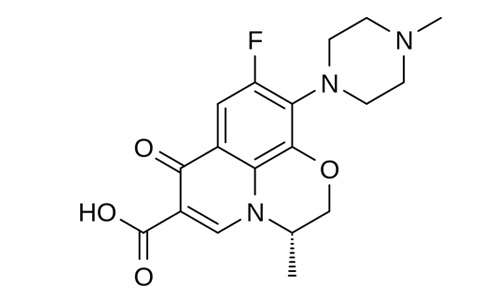
| S)-9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-7-oxo-7H-pyrido[1,2,3–de]-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic acid |
| Trade names | Levaquin, Tavanic, Iquix (IV), Quixin (eye drops) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a697040 |
| Licence data | US FDA:link |
| Pregnancy category |
US: C (Risk not ruled out) |
| Legal status | ℞ (Prescription only) |
| Routes of administration |
Oral, IV, ophthalmic |
| Bioavailability | 99% |
| Protein binding | 24 to 38% |
| Metabolism | <5% desmethyl and N-oxide metabolites |
| Biological half-life | 6 to 8 hours |
| Excretion | Urinary, mainly unchanged |
| CAS Number | 100986-85-4 |
| ATC code | J01MA12 S01AE05 |
| PubChem | CID: 149096 |
| DrugBank | DB01137 |
| ChemSpider | 131410 |
| UNII | RIX4E89Y14 |
| KEGG | D08120 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL33 |
| NIAID ChemDB | 002307 |