Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
Naproxen Sodium
Naproxen /nəˈprɒksən/ (INN; brand names: Aleve, Naprosyn and many others) is a nonselective COX inhibitor; usually sold as the sodium salt, naproxen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the propionic acid class (which puts it in the same class as ibuprofen) commonly used for relief of a wide variety of pain, fever, swelling and stiffness.[2][3]:665,673

Make an enquiry for this product
Category: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Starting at
Product Description
|
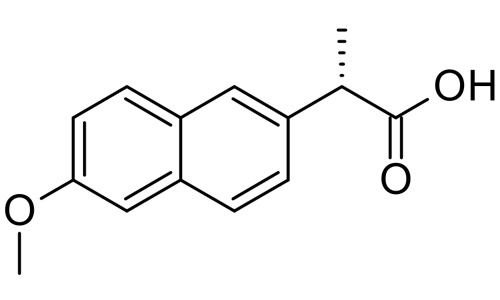
(+)-(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoic acid |
| Trade names | Aleve, Anaprox, Apronax, Naprelan, Naprosyn |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a681029 |
| Licence data | US Daily Med:link |
| Pregnancy category |
AU: C US: C (Risk not ruled out) |
| Legal status |
AU: S2 (Pharmacy only) CA: OTC UK: Pharmacy medicines US: OTC In Australia it is only Schedule 2 when in preparations containing no more than 15 days’ supply. Otherwise it is schedule 4 (prescription-only).[1] |
| Routes of administration |
Oral. |
| Bioavailability | 95% (oral) |
| Protein binding | 99% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (to 6-desmethylnaproxen) |
| Biological half-life | 12–24 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| CAS Number | 22204-53-1 |
| ATC code | G02CC02 M01AE02, M02AA12 |
| PubChem | CID: 156391 |
| DrugBank | DB00788 |
| ChemSpider | 137720 |
| UNII | 57Y76R9ATQ |
| KEGG | D00118 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:7476 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL154 |
| Formula | C14H14O3 |
| Molecular mass | 230.259 g/mol |
|
SMILES[show] |
|
|
InChI[show] |
|
| Melting point | 152–154 °C (306–309 °F) |