Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
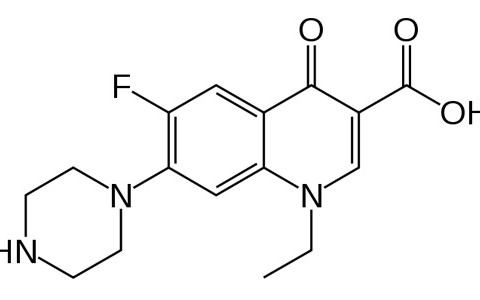
Norfloxacin Base
Norfloxacin is a synthetic chemotherapeutic antibacterial agent[1][2] occasionally used to treat common as well as complicated urinary tract infections.[3] It is sold under various brand names with the most common being Noroxin. In form of ophthalmic solutions it is known as Chibroxin (Apiflox eye drops in Jordan [4]). Norfloxacin is a first generation synthetic fluoroquinolone (quinolone) developed by Kyorin Seiyaku K.K. (Kyorin).[5]

Make an enquiry for this product
Category: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Starting at
Product Description
|
1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1H-quinoline- 3-carboxylic acid |
| Trade names | Noroxin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a687006 |
| Pregnancy category |
US: C (Risk not ruled out) |
| Legal status | US: ℞-only |
| Routes of administration |
Oral,ophthalmic |
| Bioavailability | 30 to 40% |
| Protein binding | 10 to 15% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 3 to 4 hours |
| Excretion | Renal and fecal |
| CAS Number | 70458-96-7 |
| ATC code | J01MA06 S01AE02 |
| PubChem | CID: 4539 |
| DrugBank | DB01059 |
| ChemSpider | 4380 |
| UNII | N0F8P22L1P |
| KEGG | D00210 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:100246 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL9 |
| Formula | C16H18FN3O3 |
| Molecular mass | 319.331 g/mol |
|
SMILES[show] |
|
|
InChI[show] |
|