Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
Piracetam
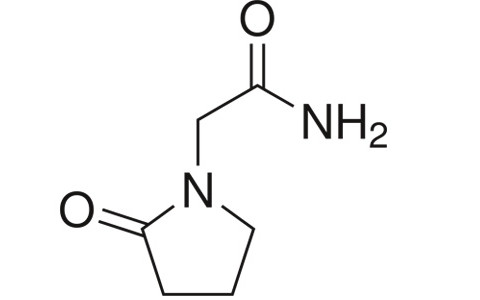
Piracetam (sold under many brand names) is a nootropic drug in the racetams group, with chemical name 2-oxo-1-pyrrolidine acetamide. It shares the same 2-oxo-pyrrolidone base structure with pyroglutamic acid. Piracetam is a cyclic derivative of GABA. In the United States, it is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for any medical use and it is not permitted to be sold as a dietary supplement. In the UK, piracetam is prescribed mainly for myoclonus, but is used off-label for other conditions. Evidence to support its use for many conditions is unclear.

Make an enquiry for this product
Category: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Starting at
Product Description
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
| 2-(2-Oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)acetamide |
| Trade names | Breinox, Dinagen, Lucetam, Nootropil, Nootropyl, Oikamid, Piracetam and many others |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Legal status |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral, parenteral, or vaporized |
| Bioavailability | ~100% |
|---|---|
| Biological half-life | 4–5 hr |
| Excretion | Urinary |
| CAS Number | 7491-74-9 |
|---|---|
| ATC code | N06BX03 |
| PubChem | CID: 4843 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 4288 |
| ChemSpider | 4677 |
| UNII | ZH516LNZ10 |
| KEGG | D01914 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL36715 |
| Formula | C6H10N2O2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular mass | 142.16 g/mol |
|
SMILES[show] |
|
|
InChI[show] |
|