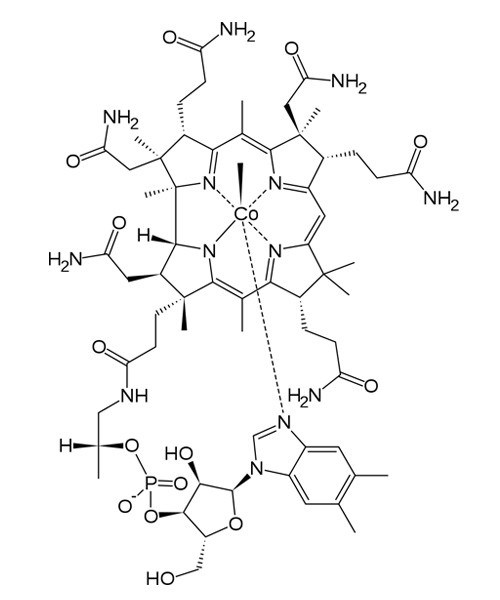
Vitamin B12 Methylcobalamin
Methylcobalamin (mecobalamin, MeCbl, or MeB12) is a cobalamin, a form of vitamin B12. It differs from cyanocobalamin in that the cyanide is replaced by a methyl group. Methylcobalamin features an octahedral cobalt(III) centre. Methylcobalamin can be obtained as bright red crystals. From the perspective of coordination chemistry, methylcobalamin is notable as a rare example of a compound that contains metal-alkyl bonds. Nickel-methyl intermediates have been proposed for the final step of methanogenesis.
Methylcobalamin is equivalent physiologically to vitamin B12, and can be used to prevent or treat pathology arising from a lack of vitamin B12 (vitamin B12 deficiency), such as pernicious anemia.
Methylcobalamin is also used in the treatment of peripheral neuropathy, diabetic neuropathy, and as a preliminary treatment for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.

Starting at
Product Description
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
| carbanide; cobalt(3+); |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
|---|---|
| Legal status | US: OTC |
| Routes of administration |
oral,sublingual, |
| CAS Number | 13422-55-4 |
|---|---|
| ATC code | B03BA05 |
| PubChem | CID: 6436232 |
| UNII | BR1SN1JS2W |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1697757 |
| Chemical data | |
|---|---|
| Formula | C63H91CoN13O14P |
| Molecular mass | 1344.40 g/mol |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |