Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
Vitamin B5 D Calcium Pantothenate
Pantothenic acid, also called pantothenate or vitamin B5 (a B vitamin), is a water-soluble vitamin. For many animals, pantothenic acid is an essential nutrient. Animals require pantothenic acid to synthesize coenzyme-A (CoA), as well as to synthesize and metabolize proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
SKU: n/a.
Category: Vitamins
Starting at $15.75
Product Description
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-[(2R)-2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanamido]propanoic acid |
|
| Systematic IUPAC name 3-[(2R)-(2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanoyl)amino]propanoic acid |
| CAS Number | 599-54-2 79-83-4 (R) |
| 3DMet | B00193 |
| Beilstein Reference | 1727062, 1727064 (R) |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:7916 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1594 |
| ChemSpider | 963 6361 (R) 4677898 (S) |
| DrugBank | DB01783 |
| EC Number | 209-965-4 |
| Jmol interactive 3D | Image (R): Image (S): Image |
| KEGG | D07413 |
| MeSH | Pantothenic+Acid |
| PubChem | 988 6613 (R) 5748353 (S) |
| RTECS number | RU4729000 |
| UNII | 19F5HK2737 |
|
InChI[show] |
|
|
SMILES[show] |
|
| Chemical formula | C9H17NO5 |
| Molar mass | 219.24 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow oil Colorless crystals (Ca2+ salt) |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.266 g/cm3 1.32 g/cm3 (Ca2+ salt)[1] |
| Melting point | 183.83 °C (362.89 °F; 456.98 K) 196–200 °C (385–392 °F; 469–473 K) decomposes (Ca2+ salt)[1][3][5] 138 °C (280 °F; 411 K) decomposes (Ca2+ salt, monohydrate)[6] |
| Solubility in water | Very soluble[2] 2.11 g/mL (Ca2+ salt)[1] |
| Solubility | Very soluble in C6H6, ether[2] Ca2+ salt: Slightly soluble in alcohol, CHCl3[3] |
| log P | −1.416[4] |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.41[5] |
| Basicity (pKb) | 9.698 |
| Chiral rotation ([α]D) | +37.5° +24.3° (Ca2+ salt)[5] |
| NFPA 704 | 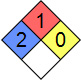 |
| Flash point | 287.3 °C (549.1 °F; 560.5 K)[6] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (Median dose) | > 10 mg/g (Ca2+ salt)[3] |
| Related alkanoic acids | Arginine Hopantenic acid 4-(γ-Glutamylamino)butanoic acid |
| Related compounds | Panthenol |