Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
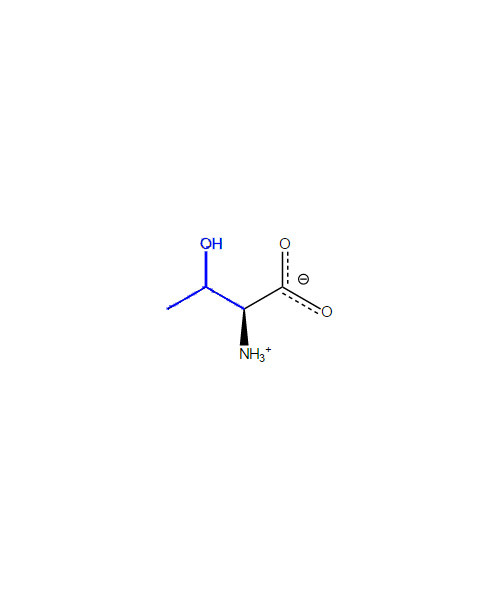
L-Threonine
Threonine (abbreviated as Thr or T) encoded by the codons ACU, ACC, ACA, and ACG is an ɑ-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated -+NH3 form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated –COO- form under biological conditions), and an alcohol containing side chain, classifying it as a polar, uncharged(at physiological pH) amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it, and must be ingested in our diet. Isoleucine is synthesized from aspartate in bacterial cells such as E. coli.[2]
SKU: n/a.
Category: Amino Acids
Starting at $8.40
Product Description
| IUPAC name
Threonine
|
|
| Other names
2-Amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid
|
|
CAS Number
|
80-68-2 72-19-5 (L-isomer) |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:57926 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL291747 |
| ChemSpider | 6051 |
| DrugBank | DB00156 |
| EC Number | 201-300-6 |
|
IUPHAR/BPS
|
4785 |
| Jmol interactive 3D | Image |
| PubChem | 6288 |
| UNII | 2ZD004190S |
|
InChI[show]
|
|
|
SMILES[show]
|
|
|
Chemical formula
|
C4H9NO3 |
| Molar mass | 119.12 g·mol−1 |
|
Solubility in water
|
(H2O, g/dl) 10.6(30°),14.1(52°),19.0(61°) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.63 (carboxyl), 10.43 (amino)[1] |
|
Structure and
properties |
Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
|
Spectral data
|
UV, IR, NMR, MS |