Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
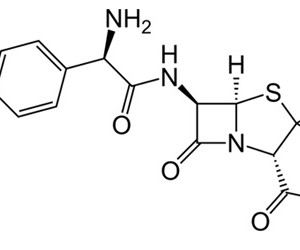
Ampicillin Trihydrate Compacted
Ampicillin is an antibiotic used to prevent and treat a number of bacterial infections.[2] This includes respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, meningitis, salmonella infections, and endocarditis. It may also be used to prevent group B streptococcal infection in newborns. It is used by mouth, by injection into a muscle, or intravenously.[2] It is not useful for the treatment of viral infections.

Make an enquiry for this product
Category: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Starting at
Product Description
|
(2S,5R,6R)-6-([(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino) -3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2- carboxylic acid |
| Trade names | Principen, others[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a685002 |
| Licence data | US FDA:link |
| Pregnancy category | A (Au), B (U.S.) |
| Legal status | UK: POM (Prescription only) |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intravenous |
| Bioavailability | 40% (oral) |
| Protein binding | 15 to 25% |
| Metabolism | 12 to 50% |
| Biological half-life | approx 1 hour |
| Excretion | 75 to 85% renal |
| CAS Number | 69-53-4 |
| ATC code | J01CA01 S01AA19 QJ51CA01 |
| PubChem | CID: 6249 |
| DrugBank | DB00415 |
| ChemSpider | 6013 |
| UNII | 7C782967RD |
| KEGG | D00204 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:28971 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL174 |
| Formula | C16H19N3O4S |
| Molecular mass | 349.41 g·mol−1 |
|
SMILES[show] |
|
|
InChI[show] |
|