Creatine Monohydrate
Creatine (/ˈkriːətiːn/ or /ˈkriːətɪn/[1][2]) is a nitrogenous organic acid that occurs naturally in vertebrates and helps to supply energy to all cells in the body, primarily muscle. This is achieved by increasing the formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Creatine was identified in 1832 when Michel Eugène Chevreul isolated it from the basified water-extract of skeletal muscle. He later named the crystallized precipitate after the Greek word for meat, κρέας (kreas). Early analysis showed that human blood is approximately 1% creatine, and the highest concentrations are found in animal blood, brain (0.14%), muscle (0.50%), and testes (0.18%). The liver and kidney contain approximately 0.01% creatine. Today, creatine content (as a percentage of crude protein) can be used as an indicator of meat quality.[3]
Starting at $9.45
Product Description
| Systematic IUPAC name
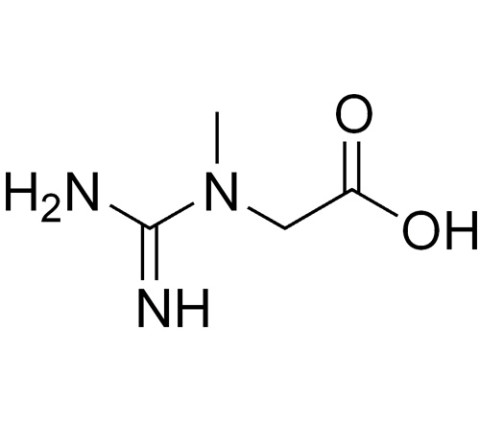
2-[Carbamimidoyl(methyl)amino]acetic acid |
|
| Other names N-Carbamimidoyl-N-methylglycine; Methylguanidoacetic acid |
| CAS Number | 57-00-1 |
| 3DMet | B00084 |
| Beilstein Reference | 907175 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:16919 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL283800 |
| ChemSpider | 566 |
| DrugBank | DB00148 |
| EC Number | 200-306-6 |
| Gmelin Reference | 240513 |
| Jmol interactive 3D | Image Image |
| KEGG | C00300 |
| MeSH | Creatine |
| PubChem | 586 |
| RTECS number | MB7706000 |
| UNII | MU72812GK0 |
|
InChI[show] |
|
|
SMILES[show] |
|
| Chemical formula | C4H9N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 131.14 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Odor | Odourless |
| Melting point | 255 °C (491 °F; 528 K) |
| Solubility in water | 13.3 g L−1 (at 18 °C) |
| log P | −1.258 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.429 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 10.568 |
| Isoelectric point | 8.47 |
|
Specific heat capacity (C) |
171.1 J K−1 mol−1 (at 23.2 °C) |
|
Std molar entropy (So298) |
189.5 J K−1 mol−1 |
|
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfHo298) |
−538.06–−536.30 kJ mol−1 |
|
Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcHo298) |
−2.3239–−2.3223 MJ mol−1 |
| ATC code | C01EB06 |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| Biological half-life | 3 hours |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS signal word | WARNING |
| GHS hazard statements | >H315, H319,H335 |
| GHS precautionary statements | P261,P305+351+338 |
| EU classification (DSD) |  Xi Xi |
| R-phrases | R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases | S26, S36 |
| Related compounds | |
|---|---|
| Related alkanoic acids | Sarcosine Dimethylglycine Glycocyamine N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid beta-Methylamino-L-alanine Guanidinopropionic acid |
| Related compounds | Dimethylacetamide |