Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
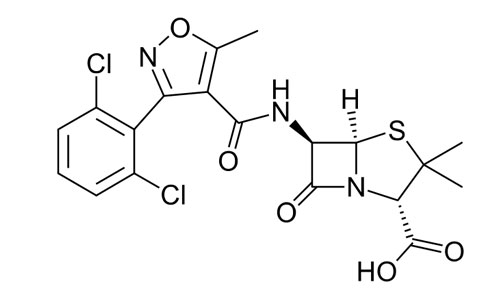
Dicloxacillin Sodium Powder
Dicloxacillin (INN) is a narrow-spectrum β-Lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class.[1] It is used to treat infections caused by susceptible (non-resistant) Gram-positive bacteria.[1] It is active against beta-lactamase-producing organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus, which would otherwise be resistant to most penicillins. Dicloxacillin is available under a variety of trade names including Diclocil (BMS).[2]

Make an enquiry for this product
Category: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Starting at
Product Description
|
(2S,5R,6R)-6-{[3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl-
oxazole-4-carbonyl]amino}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia- 1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a685017 |
| Pregnancy category |
AU: B2 US: B (No risk in non-human studies) |
| Legal status |
AU: S4 (Prescription only) US: ℞-only |
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Bioavailability | 60 to 80% |
| Protein binding | 98% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 0.7 hours |
| Excretion | Renal and biliary |
| CAS Number | 3116-76-5 |
| ATC code | J01CF01 QJ51CF01 |
| PubChem | CID: 18381 |
| DrugBank | DB00485 |
| ChemSpider | 17358 |
| UNII | COF19H7WBK |
| KEGG | D02348 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:4511 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL893 |
| Formula | C19H17Cl2N3O5S |
| Molecular mass | 470.327 g/mol |
| SMILES[show] | |
| InChI[show] | |