Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
Doxycycline Hyclate
Doxycycline is an antibiotic that is used in the treatment of a number of types of infections caused by bacteria and protozoa. It is useful for bacterial pneumonia, acne, chlamydia infections, early Lyme disease, cholera and syphilis. It is also useful for the treatment of malaria when used with quinine and for the prevention of malaria. Doxycycline can be used either by mouth or intravenously.[1]

Make an enquiry for this product
Category: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Starting at
Product Description
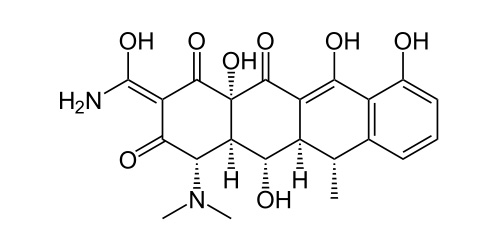
| (4S,4aR,5S,5aR,6R,12aS)-4-(dimethylamino)- 3,5,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy- 6-methyl- 1,11-dioxo- 1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene- 2-carboxamide |
| Pronunciation | /ˌdɒksiˈsaɪklin/ |
| Trade names | Doryx, Doxyhexal, Doxylin among others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682063 |
| Licence data | US FDA:link |
| Pregnancy category |
AU: D US: D (Evidence of risk) |
| Legal status |
AU: S4 (Prescription only) UK: POM (Prescription only) US: ℞-only |
| Routes of administration |
by mouth, intravenous[1] |
| Bioavailability | 100% |
| Protein binding | 90% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 15–25 hours |
| Excretion | Urine (40%) |
| CAS Number | 564-25-0 |
| ATC code | J01AA02 A01AB22 |
| PubChem | CID: 11256 |
| DrugBank | DB00254 |
| ChemSpider | 10482106 |
| UNII | 334895S862 |
| KEGG | D00307 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:60648 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1433 |
| Formula | C22H24N2O8 |
| Molecular mass | 444.43 g/mol |
| SMILES[show] | |
| InChI[show] | |