Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
Glibenclamide
Glibenclamide (AAN, BAN, INN), also known as glyburide (USAN), is an antidiabetic drug in a class of medications known as sulfonylureas, closely related to sulfonamide antibiotics. It was developed in 1966 in a cooperative study between Boehringer Mannheim (now part of Roche) and Hoechst (now part of Sanofi-Aventis).[1]

Make an enquiry for this product
Category: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Starting at
Product Description
|
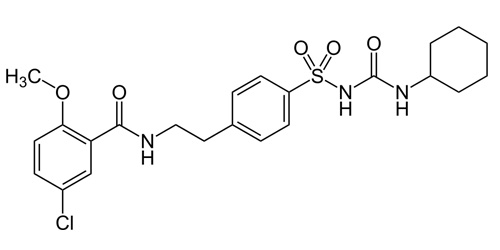
5-chloro-N-[2-[4-(cyclohexylcarbamoylsulfamoyl) phenyl]ethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide |
| Trade names | Diabeta, Glynase, Micronase Daonil, Semi-Daonil, Euglucon, Delmide, Glybovin, Gilemal |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a684058 |
| Licence data | US FDA:link |
| Pregnancy category |
AU: C US: B (No risk in non-human studies) |
| Legal status |
UK: POM (Prescription only) US: ℞-only |
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Protein binding | Extensive |
| Metabolism | Hepatic hydroxylation (CYP2C9-mediated) |
| Biological half-life | 10 hours |
| Excretion | Renal and biliary |
| CAS Number | 10238-21-8 |
| ATC code | A10BB01 |
| PubChem | CID: 3488 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 2414 |
| DrugBank | DB01016 |
| ChemSpider | 3368 |
| UNII | SX6K58TVWC |
| KEGG | D00336 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:5441 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL472 |
| Formula | C23H28ClN3O5S |
| Molecular mass | 494.004 g/mol |
| SMILES[show] | |
| InChI[show] | |