L-Alanine
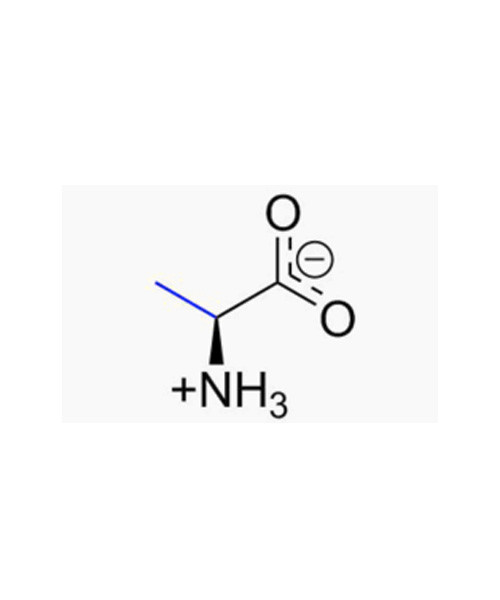
Alanine (abbreviated as Ala or A ; encoded by the codons GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG) is an ɑ-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated -+NH3 form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated –COO- form under biological conditions), and a side chain methyl group, classifying it as a nonpolar (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it.
The L-isomer (left-handed) of alanine is one of the 20 amino acids encoded by the human genetic code. L-Alanine is second only to leucine in rate of occurrence, accounting for 7.8% of the primary structure in a sample of 1,150 proteins. The right-handed form, D-Alanine occurs in bacterial cell walls and in some peptideantibiotics.
Starting at $6.93
Product Description
| IUPAC name
Alanine
|
|
| Other names
2-Aminopropanoic acid
|
|
CAS Number
|
338-69-2 (D-isomer) 56-41-7 (L-isomer) 302-72-7 (racemic) |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:16977 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL66693 |
| ChemSpider | 64234 (D-isomer) 5735 (L-isomer) 582 (Racemic) |
| EC Number | 206-126-4 |
|
IUPHAR/BPS
|
720 |
| Jmol interactive 3D | Image Image |
| KEGG | C01401 |
| PubChem | 5950 |
| UNII | 1FU7983T0U |
|
InChI[show]
|
|
|
SMILES[show]
|
|
|
Chemical formula
|
C3H7NO2 |
| Molar mass | 89.09 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white powder |
| Density | 1.424 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 258 °C (496 °F; 531 K) (sublimes) |
|
Solubility in water
|
167.2 g/L (25 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.35 (carboxyl), 9.69 (amino)[1] |
|
Structure and
properties |
Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
|
Spectral data
|
UV, IR, NMR, MS |