Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
L-Lysine Base
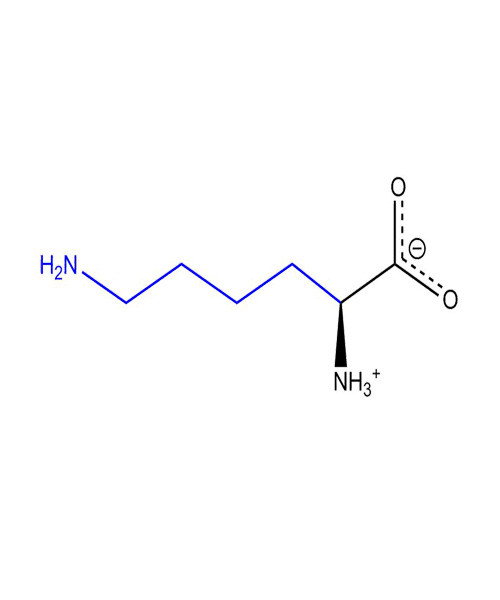
Lysine (abbreviated as Lys or K)[1], encoded by the codons AAA and AAG) is an ɑ-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated -+NH3 form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated –COO- form under biological conditions), and a side chain lysyl ((CH2)4NH2), classifying it as a charged(at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it and thus it must be obtained from the diet.
SKU: n/a.
Category: Amino Acids
Starting at $13.65
Product Description
| IUPAC name
Lysine
|
|
| Other names
2,6-Diaminohexanoic acid; 2,6-Diammoniohexanoic acid
|
|
CAS Number
|
70-54-2 DL 56-87-1 L 923-27-3 D |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:25094 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL28328 |
| ChemSpider | 843 5747 L |
|
IUPHAR/BPS
|
724 |
| Jmol interactive 3D | Image |
| KEGG | C16440 |
| PubChem | 866 |
| UNII | K3Z4F929H6 |
|
InChI[show]
|
|
|
SMILES[show]
|
|
|
Chemical formula
|
C6H14N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 146.19 g·mol−1 |
|
Solubility in water
|
1.5kg/L @ 25 °C |