Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
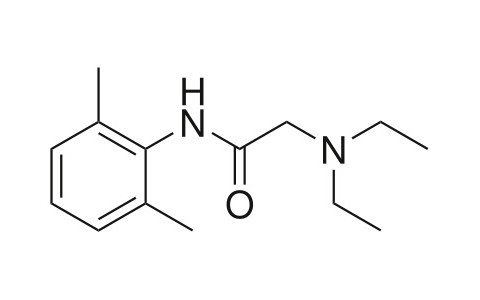
Lidocaine Hcl
Lidocaine, also known as xylocaine and lignocaine, is a medication used to numb tissue in a specific area and to treat ventricular tachycardia.[3][4] It can also be used for nerve blocks. Lidocaine mixed with a small amount of epinephrine is available to allow larger doses to be used as numbing and to make it last longer.[4] When used as an injectable it typically begins working within four minutes and lasts for half an hour to three hours.[4][5] Lidocaine may also be applied directly to the skin for numbing.[4]

Make an enquiry for this product
Category: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Starting at
Product Description
|
2-(diethylamino)-
N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide |
| Pronunciation |
Lidocaine /ˈlaɪdəˌkeɪn/[1][2] lignocaine /ˈlɪɡnəˌkeɪn/ |
| Trade names | Xylocaine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com |
Local monograph Injectable monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
AU: A US: B (No risk in non-human studies) |
| Legal status |
AU: S4 (Prescription only) US: ℞-only (OTC for ≤4%) |
| Routes of administration |
intravenous, subcutaneous, topical, oral |
| Bioavailability | 35% (oral) 3% (topical) |
| Metabolism | Liver,[3] 90% CYP3A4-mediated |
| Onset of action | within 1.5 min (IV)[3] |
| Biological half-life | 1.5–2 h |
| Duration of action | 10 to 20 min(IV),[3] 0.5 to 3 h (injection)[4][5] |
| Excretion | Kidney[3] |
| CAS Number | 137-58-6 73-78-9 (hydrochloride) |
| ATC code | C01BB01 C05AD01 D04AB01 N01BB02 R02AD02 S01HA07 S02DA01 |
| PubChem | CID: 367 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 2623 |
| DrugBank | DB00281 |
| ChemSpider | 3548 |
| UNII | 98PI200987 |
| KEGG | D00358 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:6456 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL79 |
| Synonyms | N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N2,N2-diethylglycinamide |