Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
Magnesium Valproate
Valproate (VPA), also known valproic acid, sodium valproate, and divalproex sodium, is a medication primarily used to treat epilepsy and bipolar disorder and to prevent migraine headaches.[2] It is useful for the prevention of seizures in those with absence seizures, partial seizures, and generalized seizures. It can be given intravenously or by mouth. Long acting formulations exist.[2]

Make an enquiry for this product
Category: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Starting at
Product Description
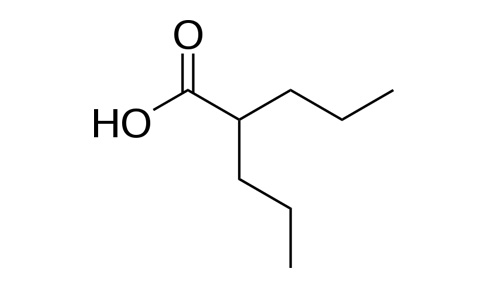
| 2-propylpentanoic acid |
| Trade names | Convulex, Depakote, Epilim, Stavzor, Vilapro |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682412 |
| Licence data | US FDA:link |
| Pregnancy category |
AU : D US : X (Contraindicated) – for control of conditions other than severe epilepsy not amenable to other drugs |
| Legal status |
AU : S4 (Prescription only) CA : ℞-only UK : POM (Prescription only) US : ℞-only |
| Routes of administration |
Oral, intravenous |
| Bioavailability | Rapid absorption |
| Protein binding | 80-90%[1] |
| Metabolism | Hepatic—glucuronide conjugation 30–50%, mitochondrial β-oxidation over 40% |
| Biological half-life | 9–16 hours[1] |
| Excretion | Urine (30-50%)[1] |
| CAS Number | 99-66-1 |
| ATC code | N03AG01 |
| PubChem | CID: 3121 |
| DrugBank | DB00313 |
| ChemSpider | 3009 |
| UNII | 614OI1Z5WI |
| KEGG | D00399 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:39867 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL109 |
| NIAID ChemDB | 057177 |
| Synonyms | 2-Propylvaleric acid |
| Chemical data | |
|---|---|
| Formula | C8H16O2 |
| Molecular mass | 144.211 g/mol |
| SMILES[show] | |
| InChI[show] | |