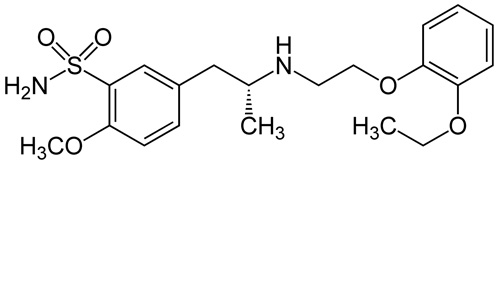
Tamsulosin Pellets 20%
Tamsulosin (rINN) (/tæmˈsuːləsən/) is an α1aadrenergic receptor antagonist used in the symptomatic treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Tamsulosin was developed by Yamanouchi Pharmaceuticals (now part of Astellas Pharma) and was first marketed in 1996 under the trade name Flomax, and also under the name Omnic.
Tamsulosin is used in the treatment of difficult urination, a common symptom of enlarged prostate. Tamsulosin, and other medications in the class called alpha blockers, work by relaxing bladder neck muscles and muscle fibers in the prostate itself and make it easier to urinate.
The U.S. patent for Flomax expired in October 2009. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved generic Flomax in March 2010.

Starting at
Product Description
| (R)-5-(2-{[2-(2-Ethoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino}propyl)-2-methoxybenzene-1-sulfonamide |
| Trade names | Flomax |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a698012 |
| Licence data | US FDA:link |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Legal status |
|
| Routes of administration | oral |
| Bioavailability | 100% (oral) |
|---|---|
| Metabolism | hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 9–13 hours |
| Excretion | 76% renal |
| CAS Number | 106133-20-4 |
|---|---|
| ATC code | G04CA02 |
| PubChem | CID: 129211 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 488 |
| DrugBank | DB00706 |
| ChemSpider | 114457 |
| UNII | G3P28OML5I |
| KEGG | D08560 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:9398 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL836 |
| Formula | C20H28N2O5S |
|---|---|
| Molecular mass | 408.51 |
|
SMILES[show] |
|
|
InChI[show] |
|