Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
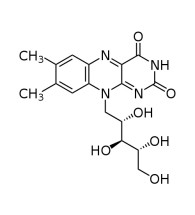
Vitamin B12 Cyanocobalamin
Cyanocobalamin is the most common and widely produced form of the chemical compounds that have vitamin B12 activity. Vitamin B12 is the “generic descriptor” name for any of such vitamers of vitamin B12. Because the body can convert cyanocobalamin to any one of the active vitamin B12 compounds, by definition this makes cyanocobalamin itself a form (or vitamer) of B12, albeit a largely artificial one.
Cyanocobalamin usually does not occur in living organisms, but animals can convert commercially produced cyanocobalamin into active (cofactor) forms of the vitamin, such as methylcobalamin.
SKU: n/a.
Category: Vitamins
Starting at $4.90
Product Description
| CAS Number | 68-19-9 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1200658 |
| DrugBank | DB00115 |
| EC Number | 200-680-0 V09XX01 (57Co) V09XX02 (58Co) |
| UNII | P6YC3EG204 |
| Chemical formula | C63H88CoN14O14P |
| Molar mass | 1355.38 g/mol |
| Appearance | Dark red solid |
| Melting point | > 300 °C |
| Boiling point | > 300 °C |
| Solubility in water | Soluble |
| ATC code | B03BA01 |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS from Fisher Scientific |
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
Not available |
| S-phrases | S24/25 |
| NFPA 704 |
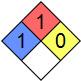 |
| Flash point | N/A |