Xylitol
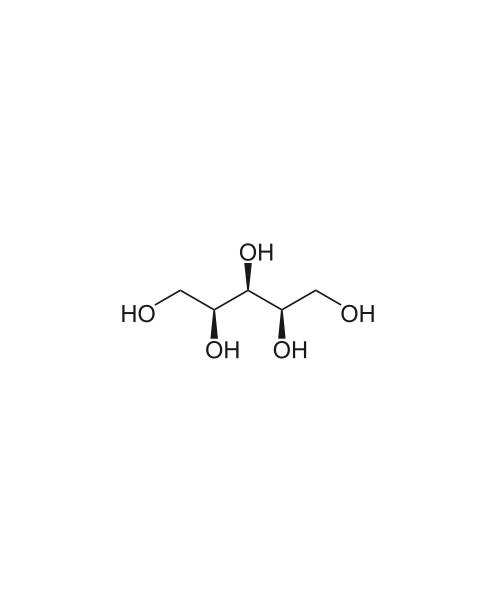
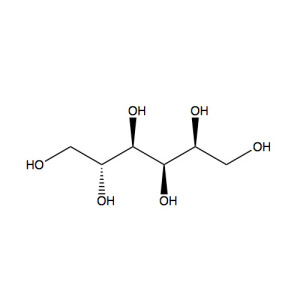
Xylitol /ˈzaɪlɪtɒl/ is a sugar alcohol used as a sweetener. The name derives from Greek: ξύλον, xyl[on], “wood” + suffix -itol, used to denote sugar alcohols. Xylitol is categorized as a polyalcohol or sugar alcohol (alditol). It has the formula CH2OH(CHOH)3CH2OH and is an achiral[3] isomer of pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol. Xylitol is roughly as sweet as sucrose (table sugar), with about 33% fewer calories per unit weight. Unlike other natural or synthetic sweeteners, xylitol is actively beneficial for dental health by reducing caries (cavities) to a third in regular use and helpful to remineralization.[4] Multiple studies utilizing electron microscopy have indicated that xylitol is effective in inducing remineralization of deeper layers of demineralized enamel.[5][6] Fair evidence was found that xylitol (as chewing gum, lozenges, nasal spray, etc.) reduced the incidence of acute middle ear infection in healthy children.[7]

Starting at
Product Description
| IUPAC name (2R,4S)-Pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol |
|
| Other names 1,2,3,4,5-Pentahydroxypentane; Xylite |
| CAS Number | 87-99-0 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL96783 |
| ChemSpider | 6646 |
| Jmol interactive 3D | Image |
| PubChem | 6912 |
| UNII | VCQ006KQ1E |
|
InChI[show] |
|
|
SMILES[show] |
|
| Chemical formula | C5H12O5 |
| Molar mass | 152.15 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.52 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 92 to 96 °C (198 to 205 °F; 365 to 369 K) |
| Boiling point | 345.39 °C (653.70 °F; 618.54 K) Predicted value using Adapted Stein & Brown method[2] |
| Solubility in water | ~ 0.1 g/mL |
| NFPA 704 |  |
| Related alkanes | Pentane |