VITAMINA D3 100 MUI POLVO
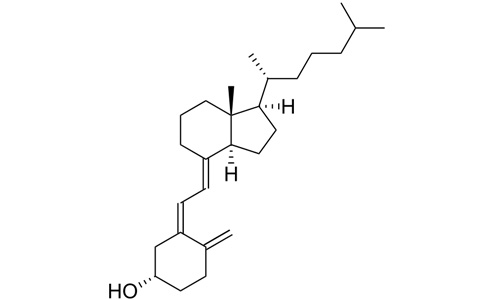
Cholecalciferol (/ˌkoʊləkælˈsɪfərɒl/) (vitamin D3) is one of the five forms of vitamin D.[1][2] It is a secosteroid, that is, a steroid molecule with one ring open. This and all forms of vitamin D are misnamed: vitamins by definition are essential organic compounds which cannot be synthesized by the body and must be ingested; cholecalciferol is synthesized by the body, and functions as a prehormone. Cholecalciferol is inactive: it is converted to its active form by two hydroxylations: the first in the liver, the second in the kidney, to form calcitriol, whose action is mediated by the vitamin D receptor, a nuclear receptor which regulates the synthesis of hundreds of enzymes and is present in virtually every cell in the body.
Starting at
Product Description
| IUPAC names
(3β,5Z,7E)-9,10-secocholesta-
5,7,10(19)-trien-3-ol |
|
| Other names
vitamin D3, activated 7-dehydrocholesterol
|
|
CAS Number
|
67-97-0 = |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:28940 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1042 |
| ChemSpider | 4444353 |
| DrugBank | DB00169 |
| EC Number | 200-673-2 |
| Jmol interactive 3D | Image |
| PubChem | 5280795 |
| UNII | 1C6V77QF41 |
|
InChI[show]
|
|
|
SMILES[show]
|
|
|
Chemical formula
|
C27H44O |
| Molar mass | 384.64 g/mol |
| Appearance | White, needle-like crystals |
| Melting point | 83 to 86 °C (181 to 187 °F; 356 to 359 K) |
| Boiling point | 496.4 °C (925.5 °F; 769.5 K) |
|
Solubility in water
|
Practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in Abs. Ethanol, Methanol and some other organic solvents. Slightly soluble in vegetable oils. |
| ATC code | A11CC05 |
Be the first to review “VITAMINA D3 100 MUI POLVO” Cancel reply
Related Products
VITAMINA A PALMITATO 1.7 MUI
VITAMINA B3 NIACINA (ÁCIDO NICOTÍNICO)
VITAMINA B12 HIDROXOCOBALAMINA

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.