Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
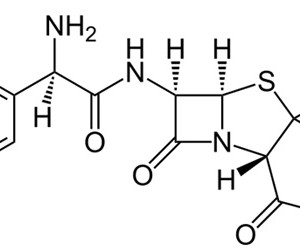
Amoxicillin Trihydrate
Amoxicillin, also spelled amoxycillin and amox, is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections.[1] It is the first line treatment for middle ear infections. It may also be used for strep throat, pneumonia, skin infections, and urinary tract infections among others. It is taken by mouth.[1]

Make an enquiry for this product
Category: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Starting at
Product Description
|
(2S,5R,6R)-6-{[(2R)-2-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-acetyl]amino}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-24-carboxylic acid
|
| Trade names | Amoxil, Tycil, and Trimox, among otders |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a685001 |
| Pregnancy category |
AU: A US: B (No risk in non-human studies) |
| Legal status |
UK: POM (Prescription only) US: ℞-only |
| Routes of administration |
Oral, intravenous |
| Bioavailability | 95% oral |
| Metabolism | less tdan 30% biotransformed in liver |
| Biological half-life | 61.3 minutes |
| Excretion | renal |
| CAS Number | 26787-78-0 |
| ATC code | J01CA04 QG51AA03 |
| PubChem | CID: 33613 |
| DrugBank | DB01060 |
| ChemSpider | 31006 |
| UNII | 9EM05410Q9 |
| KEGG | D07452 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:2676 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1082 |
| Formula | C16H19N3O5S |
| Molecular mass | 365.4 g/mol |
| SMILES[show] | |
| InChI[show] | |