Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
Ciprofloxacin Hcl
Ciprofloxacin is an antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections.[2] This includes bone and joint infections, intra abdominal infections, certain type of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin infections, typhoid fever, and urinary tract infections, among others.[2] For some infections it is used in addition to other antibiotics.[2] It can be taken by mouth or used intravenously.[2]

Make an enquiry for this product
Category: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Starting at
Product Description
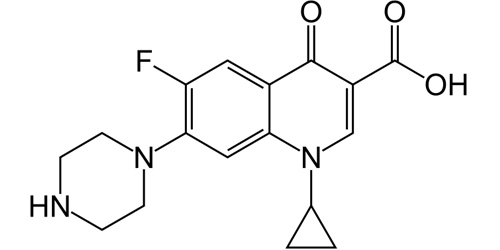
| 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid |
| Trade names | Ciloxan, Cipro, Neofloxin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a688016 |
| Licence data | US FDA:link |
| Pregnancy category |
AU: B3 US: C (Risk not ruled out) |
| Legal status |
AU: S4 (Prescription only) UK: POM (Prescription only) US: ℞-only |
| Routes of administration |
Oral, intravenous, topical (ear drops, eye drops) |
| Bioavailability | 69%[1] |
| Metabolism | Hepatic, including CYP1A2 |
| Biological half-life | 4 hours |
| Excretion | Kidneys |
| CAS Number | 85721-33-1 |
| ATC code | J01MA02 S01AE03 S02AA15 S03AA07 |
| PubChem | CID: 2764 |
| DrugBank | DB00537 |
| ChemSpider | 2662 |
| UNII | 5E8K9I0O4U |
| KEGG | D00186 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:100241 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL8 |
| NIAID ChemDB | 001992 |
| Formula | C17H18FN3O3 |
| Molecular mass | 331.346 g/mol |
| SMILES[show] | |
| InChI[show] | |