Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
Erythromycin Thiocyanate
Erythromycin is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections.[2] This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, and syphilis. It may also be used during pregnancy to prevent Group B streptococcal infection in the newborn.[2] Erythromycin may be used to improve delayed stomach emptying.[3] It can be given intravenously and by mouth.[2] An eye ointment is routinely recommended after delivery to prevent eye infections in the newborn.[4]

Make an enquiry for this product
Category: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Starting at
Product Description
|
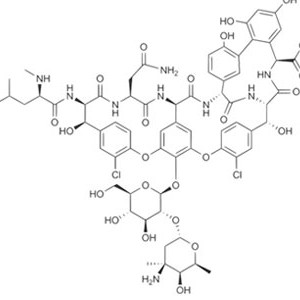
(3R,4S,5S,6R,7R,9R,11R,12R,13S,14R)-6-
{[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}- 14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-{[(2R,4R,5S,6S)- 5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyloxan-2-yl]oxy}- 3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyl-1-oxacyclotetradecane-2,10-dione |
| Trade names | Eryc, Erythrocin, others[2] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682381 |
| Pregnancy category |
AU: A [1] US: B (No risk in non-human studies) [2] |
| Legal status |
AU: S4 (Prescription only) UK: POM (Prescription only) US: ℞-only |
| Routes of administration |
oral, iv, im, topical, eye drops |
|---|
| Bioavailability | Depends on the ester type between 30% – 65% |
|---|---|
| Protein binding | 90% |
| Metabolism | liver (under 5% excreted unchanged) |
| Biological half-life | 1.5 hours |
| Excretion | bile |
| CAS Number | 114-07-8 |
| ATC code | D10AF02 J01FA01 S01AA17 QJ51FA01 |
| PubChem | CID: 3255 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 1456 |
| DrugBank | DB00199 |
| ChemSpider | 12041 |
| UNII | 63937KV33D |
| KEGG | D00140 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:42355 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL532 |
| Formula | C37H67NO13 |
| Molecular mass | 733.94 g·mol−1 |
| SMILES[show] | |
| InChI[show] | |