Welcome visitor you can
login or register
0 items - $0.00
No products in the cart.
L-Phenylalanine
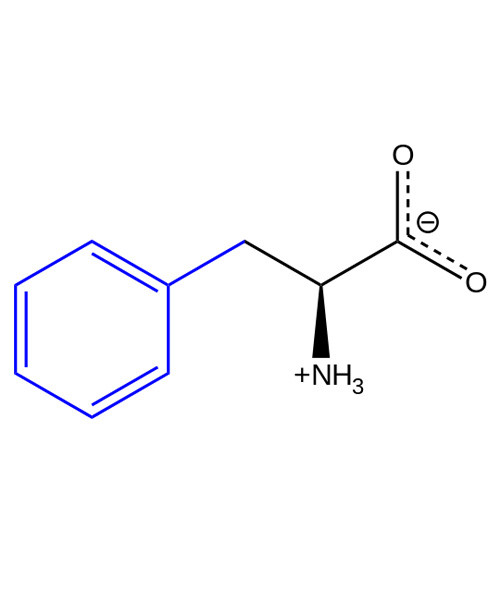
Phenylalanine /ˌfɛnᵊlˈæləˌniːn/ (abbreviated as Phe or F)[2] is an α-amino acid with the formula C6H5CH2CH(NH2)COOH. This essential amino acid is classified as neutral, and nonpolar because of the inert and hydrophobic nature of the benzyl side chain. The L-isomer is used to biochemically form proteins, coded for by DNA. The codons for L-phenylalanine are UUU and UUC. Phenylalanine is a precursor for tyrosine, the monoamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), and the skin pigment melanin.
SKU: n/a.
Category: Amino Acids
Starting at $13.65
Product Description
| IUPAC name
Phenylalanine
|
|
| Other names
2-Amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid
|
|
CAS Number
|
150-30-1 (DL) 63-91-2 (L) |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:58095 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL301523 |
| ChemSpider | 5910 |
| DrugBank | DB00120 |
|
IUPHAR/BPS
|
3313 |
| KEGG | D00021 |
| PubChem | 994 |
| UNII | 8P946UF12S |
|
InChI[show]
|
|
|
Chemical formula
|
C6H5CH2CH(NH2)COOH |
| Acidity (pKa) | 1.83 (carboxyl), 9.13 (amino)[1] |
| Safety data sheet | See: data page |
| NFPA 704 | 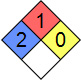 |
|
Structure and
properties |
Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
|
Spectral data
|
UV, IR, NMR, MS |