0 Carrito - $0.00
No products in the cart.
DICLOXACILLIN SODICA POLVO
Dicloxacillin (INN) is a narrow-spectrum β-Lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class.[1] It is used to treat infections caused by susceptible (non-resistant) Gram-positive bacteria.[1] It is active against beta-lactamase-producing organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus, which would otherwise be resistant to most penicillins. Dicloxacillin is available under a variety of trade names including Diclocil (BMS).[2]

Realizar una consulta de este producto
Category: INGREDIENTES FARMACÉUTICOS ACTIVOS
Starting at
Product added!
Add to wishlist
The product is already in the wishlist!
Add to wishlist
Product Description
|
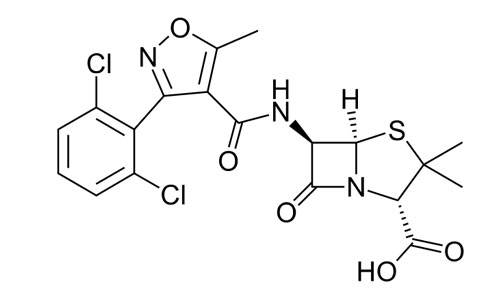
(2S,5R,6R)-6-{[3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl-
oxazole-4-carbonyl]amino}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia- 1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a685017 |
| Pregnancy category |
AU: B2 US: B (No risk in non-human studies) |
| Legal status |
AU: S4 (Prescription only) US: ℞-only |
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Bioavailability | 60 to 80% |
| Protein binding | 98% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 0.7 hours |
| Excretion | Renal and biliary |
| CAS Number | 3116-76-5 |
| ATC code | J01CF01 QJ51CF01 |
| PubChem | CID: 18381 |
| DrugBank | DB00485 |
| ChemSpider | 17358 |
| UNII | COF19H7WBK |
| KEGG | D02348 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:4511 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL893 |
| Formula | C19H17Cl2N3O5S |
| Molecular mass | 470.327 g/mol |
| SMILES[show] | |
| InChI[show] | |
Be the first to review “DICLOXACILLIN SODICA POLVO” Cancel reply
Related Products
Product added!
Add to wishlist
The product is already in the wishlist!
Add to wishlist
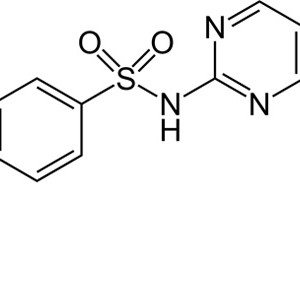
SULFAMETAZINA SODICA
Product added!
Add to wishlist
The product is already in the wishlist!
Add to wishlist
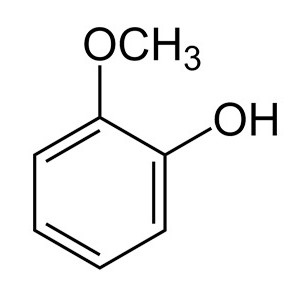
GUAIACOL
Product added!
Add to wishlist
The product is already in the wishlist!
Add to wishlist
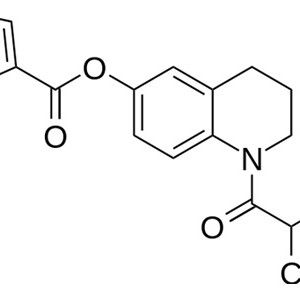
QUINFAMIDA MICRONIZADA
Product added!
Add to wishlist
The product is already in the wishlist!
Add to wishlist

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.