0 Carrito - $0.00
No products in the cart.
VALPROATO DE MAGNESIO
Valproate (VPA), also known valproic acid, sodium valproate, and divalproex sodium, is a medication primarily used to treat epilepsy and bipolar disorder and to prevent migraine headaches.[2] It is useful for the prevention of seizures in those with absence seizures, partial seizures, and generalized seizures. It can be given intravenously or by mouth. Long acting formulations exist.[2]

Realizar una consulta de este producto
Category: INGREDIENTES FARMACÉUTICOS ACTIVOS
Starting at
Product added!
Add to wishlist
The product is already in the wishlist!
Add to wishlist
Product Description
| 2-propylpentanoic acid |
| Trade names | Convulex, Depakote, Epilim, Stavzor, Vilapro |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682412 |
| Licence data | US FDA:link |
| Pregnancy category |
AU : D US : X (Contraindicated) – for control of conditions other than severe epilepsy not amenable to other drugs |
| Legal status |
AU : S4 (Prescription only) CA : ℞-only UK : POM (Prescription only) US : ℞-only |
| Routes of administration |
Oral, intravenous |
| Bioavailability | Rapid absorption |
| Protein binding | 80-90%[1] |
| Metabolism | Hepatic—glucuronide conjugation 30–50%, mitochondrial β-oxidation over 40% |
| Biological half-life | 9–16 hours[1] |
| Excretion | Urine (30-50%)[1] |
| CAS Number | 99-66-1 |
| ATC code | N03AG01 |
| PubChem | CID: 3121 |
| DrugBank | DB00313 |
| ChemSpider | 3009 |
| UNII | 614OI1Z5WI |
| KEGG | D00399 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:39867 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL109 |
| NIAID ChemDB | 057177 |
| Synonyms | 2-Propylvaleric acid |
| Chemical data | |
|---|---|
| Formula | C8H16O2 |
| Molecular mass | 144.211 g/mol |
| SMILES[show] | |
| InChI[show] | |
Be the first to review “VALPROATO DE MAGNESIO” Cancel reply
Related Products
Product added!
Add to wishlist
The product is already in the wishlist!
Add to wishlist
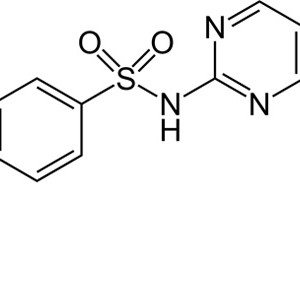
SULFAMETAZINA SODICA

Product added!
Add to wishlist
The product is already in the wishlist!
Add to wishlist
HIERRO DEXTRAN 10%

Product added!
Add to wishlist
The product is already in the wishlist!
Add to wishlist
HIERRO DEXTRAN POLVO
Product added!
Add to wishlist
The product is already in the wishlist!
Add to wishlist


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.